Special offers from our partners!

Find Replacement BBQ Parts for 20,308 Models. Repair your BBQ today.
7-295
EXPD(P)
1
2
3
4
6
6
7
8
7.12 Special function instructions
7.12.22 Exponent operation on floating-point data (Double precision) (EXPD(P))
Program Example
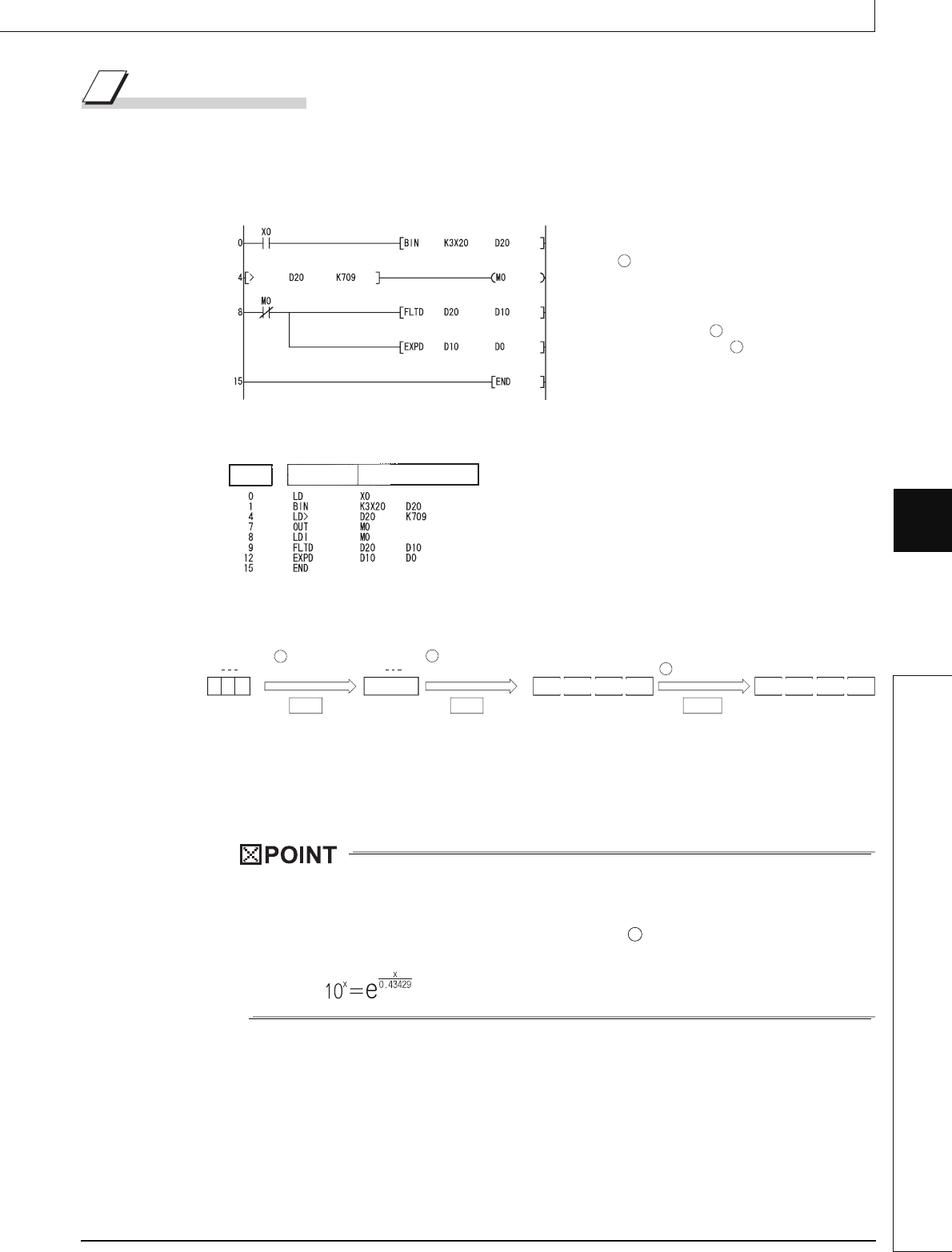
(1) The following program performs an exponent operation on the value set by the 2 BCD digits
at X20 to X31, and stores the results as a 64-bit floating decimal point real number at D0 to
D3.
[Ladder Mode]
[List Mode]
[Operations involved when value designated by X20 to X31 is 13]
*1: The operation result will be under 2
1024
if the BCD value of X20 to X31 is less than 709, from the calculation
loge 2
1024
= 709.7832.
Because setting a value of over 710 will return an operation error, turn M0 ON if a value of over 710 has been
set to avoid the error.
Conversion from natural logarithm to common logarithm
In the CPU module, calculation is made using a natural logarithm.
To obtain a common logarithm value, enter in, a common logarithm value
divided by 0.43429.
Inputs data used for exponent
operation ( ).
Converts the input data into a 64-bit
floating-point real number ( ).
Executes exponent operation ( ).
Checks the range of the value used
for operation. *1
1
2
3
Step Instruction
Device
X31
BCD value
0
D20
13
X20
Conversion
to BIN
BIN
b15 b0
BIN value
13
Conversion to
floating-point
FLTD
EXP operation
EXPD
D11
13
D10D13 D12
D1
442413.4
D0D3 D2
64-bit floating-point
real number
64-bit floating-point
real number
1
2
3
S


















