Special offers from our partners!

Find Replacement BBQ Parts for 20,308 Models. Repair your BBQ today.
6-81
FLTD(P),DFLTD(P)
1
2
3
4
4
6
7
8
6.3 Data conversion instructions
6.3.4
Conversion from BIN 16 and 32-bit data to floating decimal point (Double precision)
(FLTD(P),DFLTD(P))
6.3.4 Conversion from BIN 16 and 32-bit data to floating decimal
point (Double precision) (FLTD(P),DFLTD(P))
FLTD(P),DFLTD(P)
Function
FLTD
(1) Converts 16-bit BIN data designated by to 64-bit floating decimal point type real number,
and stores at device number designated by .
(2) BIN values between 32768 to 32767 can be designated by .
DFLTD
(1) Converts 32-bit BIN data designated by to 64-bit floating decimal point type real number,
and stores at device number designated by .
(2) BIN values between 2147483648 to 2147483647 can be designated by +1 and .
: Integer data to be converted to 64-bit floating decimal point data or head number of the devices where the
integer data is stored (BIN 16/32 bits)
:
Head number of the devices where the converted 64-bit floating decimal point data will be stored
(real number)
Setting
Data
Internal Devices
R, ZR
J\
U\G
Zn
Constants
K, H
Other
Bit Word Bit Word
–– –– ––
–– –– –– ––
Universal
Basic
Process
High
performance
Redundant
P
Command
Command
S D
S D
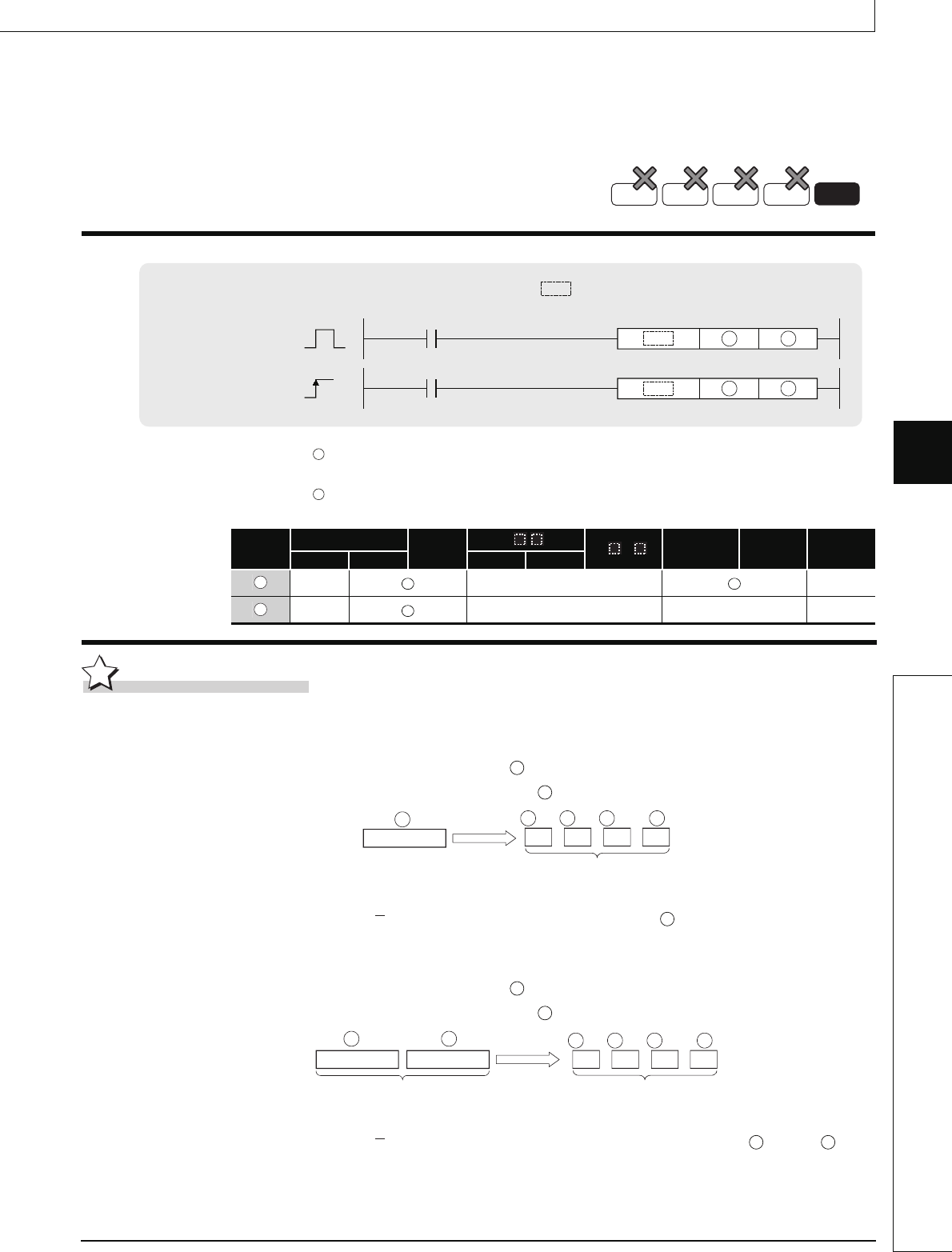
FLTD, DFLTD
FLTDP, DFLTDP
indicates an instruction symbol of FLTD/DFLTD.
S
D
S
D
S
D
BIN 16 bits
S
+3
64-bit floating-point
real number
D
+2
D
D
+1
D
S
S
D
BIN 32 bits
Upper 16 bits Lower 16 bits
+1
S S
+3
64-bit floating-point
real number
D
+2
D D
+1
D
S S


















