Special offers from our partners!

Find Replacement BBQ Parts for 20,308 Models. Repair your BBQ today.
7-255
COS(P)
1
2
3
4
6
6
7
8
7.12 Special function instructions
7.12.3 COS operation on floating-point data (Single precision) (COS(P))
Operation Error
(1) In any of the following cases, an operation error occurs, the error flag (SM0) turns ON, and
an error code is stored into SD0.
• The value of the specified device is 0.
*2
(For the Basic model QCPU, High Performance model QCPU, Process CPU, Redundant
CPU) (Error code: 4100)
*2: There are CPU modules that will not result in an operation error if 0 is specified. For details, refer to 3.2.4.
• The result exceeds the following range (Operation results in an overflow)
(For the Universal model QCPU only)
2
128
| Operation result | (Error code: 4141)
• The value of the specified device is 0, unnormalized number, nonnumeric, and ± .
(For the Universal model QCPU only) (Error code: 4140)
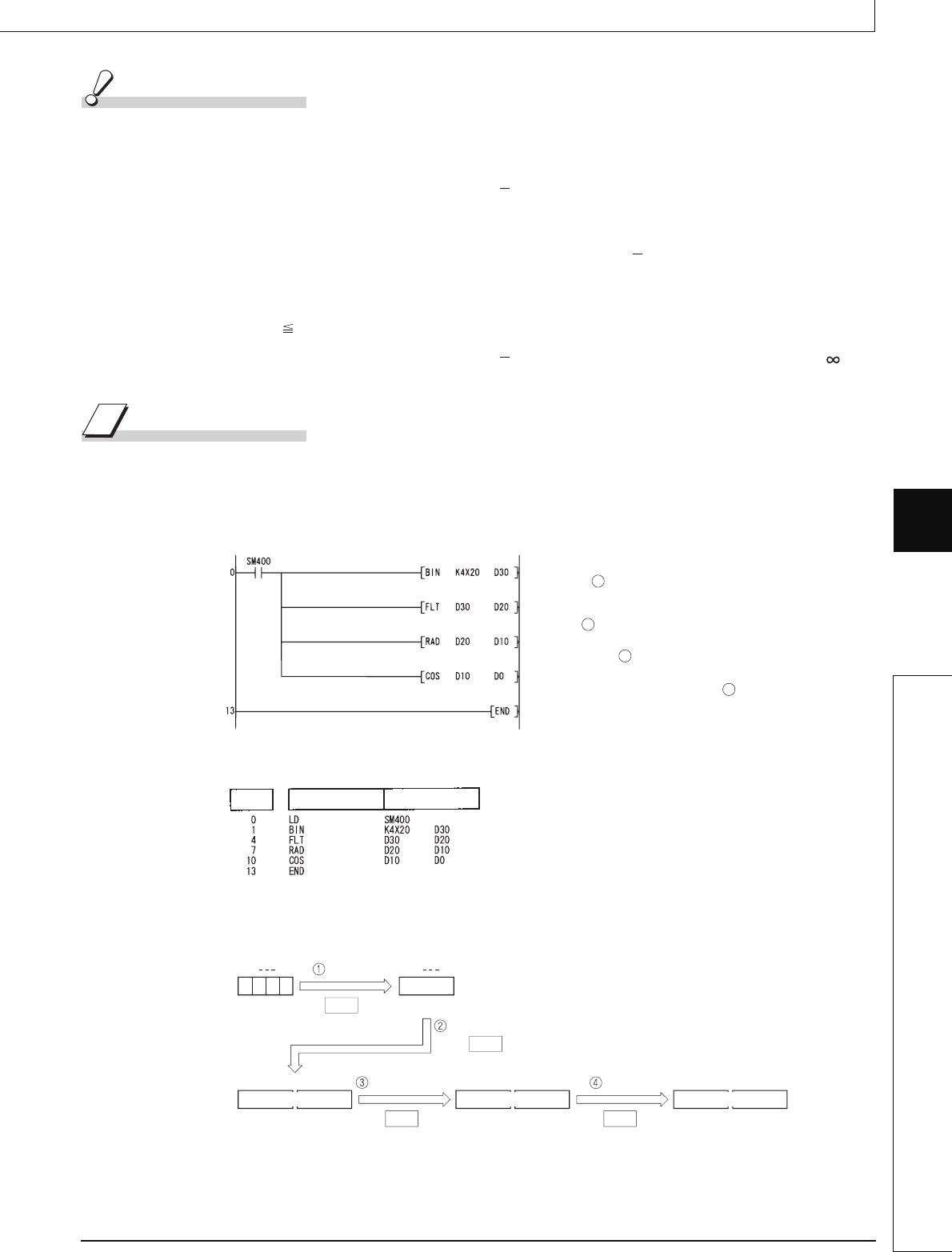
Program Example
(1) The following program performs a COS operation on the angle data designated by the 4
BCD digits from X20 to X2F, and stores results as 32-bit floating decimal point type real
numbers at D0 and D1.
[Ladder Mode]
[List Mode]
[Operations involved when X20 to X2F designate a value of 60]
Inputs an angle used for COS
operation ( ).
Converts the input angle into
a 32-bit floating-point real
number ( ).
Converts the converted angle into
a radian value ( ).
Executes COS operation
using the converted radian value ( ).
1
2
3
4
Step Instruction Device
Conversion to radian
32-bit floating-point
real number
D21
D20
RAD
COS operation
32-bit floating-point
real number
D11
D10
COS
32-bit floating-point
real number
D1
D0
X2F
BCD value
0
D30
060
X20
Conversion to BIN
BIN
b15
b0
BIN value
Conversion to floating-point
FLT
60
60
1
.
047
1
98 0
.
500000


















