Special offers from our partners!

Find Replacement BBQ Parts for 20,308 Models. Repair your BBQ today.
2-2
2.1 Types of Instructions
The major types of CPU module instructions consist of sequence instructions, basic instructions,
application instructions, data link instructions, QCPU instructions and redundant system
instructions. These types of instructions are listed in Table 2.1 below.
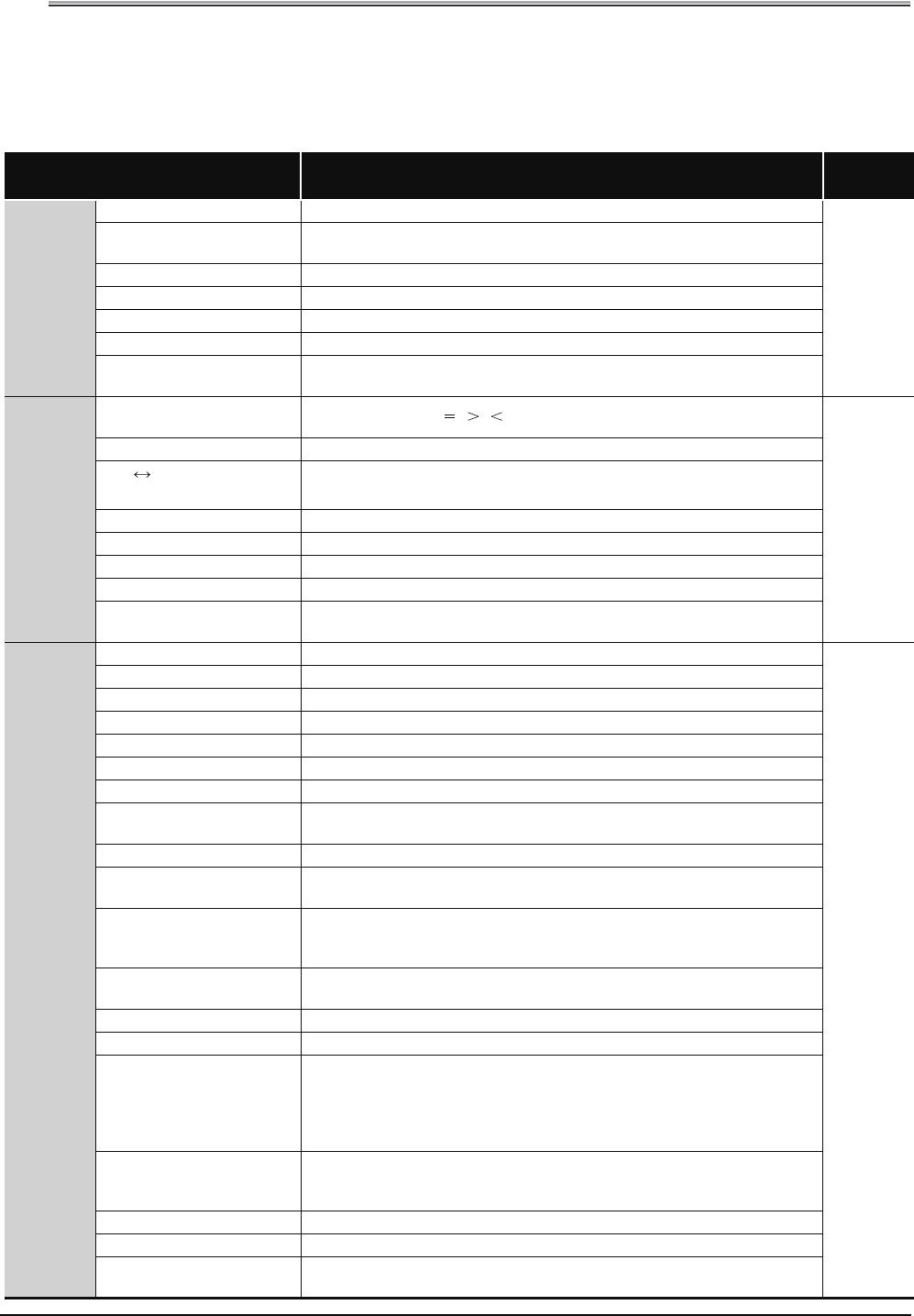
Table 2.1 Types of Instructions
Types of Instruction Meaning
Reference
Chapter
Sequence
instruction
Contact instruction Operation start, series connection, parallel connection
5
Association instruction
Ladder block connection, store/read operation results, creation of pulses from
operation results
Output instruction Bit device output, pulse output, output reversal
Shift instruction Bit device shift
Master control instruction Master control
Termination instruction Program termination
Other instruction
Program stop, instructions such as no operation which do not fit in the above
categories
Basic
instruction
Comparison operation
instruction
Comparisons such as , ,
6
Arithmetic operation instruction Addition, subtraction, multiplication or division of BIN or BCD
BCD BIN conversion
instruction
Conversion from BCD to BIN and from BIN to BCD
Data transfer instruction Transmits designated data
Program branch instruction Program jumps
Program run control instruction Enables or inhibits interrupt programs
I/O refresh Executes partial refresh
Other convenient instruction
Instructions for: Counter increment/decrement, teaching timer, special function timer,
rotary table shortest direction control, etc.
Application
instruction
Logical operation instruction Logical operations such as logical sum, logical product, etc.
7
Rotation instruction Rotation of designated data
Shift instruction Shift of designated data
Bit processing instruction Bit set and reset, bit test, batch reset of bit devices
Data processing instruction 16-bit data searches, data processing such as decoding and encoding
Structure creation instruction Repeated operation, subroutine program calls, indexing in ladder units
Table operation instruction Data table read/write
Buffer memory access
instruction
Data read/write from/to an intelligent function module
Display instruction Print ASCII code, LED character display, etc.
Debugging and failure
diagnosis instruction
Check, status latch, sampling trace, program trace
Character string processing
instruction
Conversion between BIN/BCD and ASCII;conversion between BIN and character
string; conversion between floating decimal point data and character strings,
character string processing, etc.
Special function instruction
Trigonometric functions, conversion between angles and radians, exponential
operations, automatic logarithms, square roots
Data control instruction Upper and lower limit controls, dead band controls, zone controls
Switching instruction File register block No. switches, designation of file registers and comment files
Clock instruction
Reading/writing of the values of year, month, day, hour, minute, second, and day of
the week; addition/subtraction of the values of hour, minute, and second; conversion
of the values of hour, minute, and second into second; comparison between the
values of year, month, and day; and comparison between the values of hour, minute,
and second
Expansion clock instruction
Reading of the values of year, month, day, hour, minute, second, millisecond, and
day of the week; addition/subtraction of the values of hour, minute, second, and
millisecond
Peripheral device instruction I/O to peripheral devices
Program control instruction Instructions to switch program execution conditions
Other instruction
Instructions that do not fit in the above categories, such as watchdog timer reset
instructions and timing clock instructions